Printed Circuit Boards
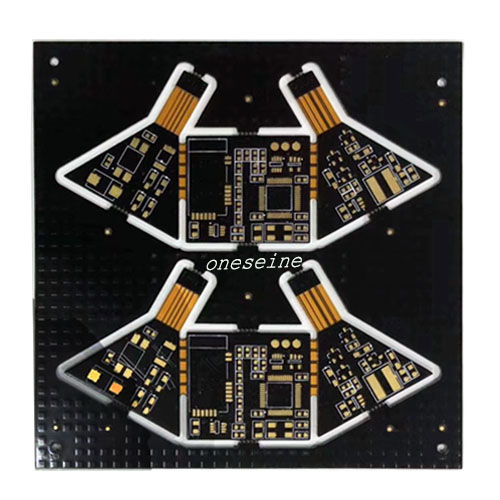
6 Layer Customized Rigid Flex Circuit PCB From Shenzhen Manufacture
- pcb rigid flex flexible pcb prototype polyimide flex rigid flex circuit boards rigid flexible printed circuit board flex board pcb flexible pcb assembly flat flex pcb semi rigid flex pcb rigid flex ci
- 6 layer flex pcb
- flex pcb prototype
- multilayer flex pcb
- Product description: pcb rigid flex flexible pcb prototype polyimide flex rigid flex circuit boards rigid flexible printed circuit board flex board pcb flexible pcb assembly flat flex pcb semi rigid flex pcb rigi
6 Layer Customized Rigid Flex Circuit PCB From Shenzhen Manufacture
PCB Quick details:
Number of layer:6
Board thickness:Rigid part:1.2mm Flex part:0.1mm
Brand: ONESEINE
Sample order:Acceptable
Application: Electronics products
Surface finish:Immersion gold
Item:rigid-flex PCB boards
Rigid-flex PCBs (printed circuit boards) are a type of PCB that combines rigid and flexible circuit board materials within the same board. This design allows for a more compact and versatile PCB solution compared to traditional rigid PCBs.
The key components of a rigid-flex PCB are:
1. Rigid Layers:
- These are the standard rigid PCB layers, typically made of fiberglass-reinforced epoxy resin (FR-4).
- They provide structural support and accommodate surface mount components and other rigid elements.
2. Flexible Layers:
- These layers are made of flexible materials, such as polyimide or polyester films.
- They allow the PCB to bend, flex, and conform to specific shapes or accommodate movement within the application.
3. Interconnections:
- The rigid and flexible layers are connected using plated through-holes or other interconnection methods.
- This allows for electrical signals and power to be transferred between the rigid and flexible sections.
The advantages of rigid-flex PCBs include:
- Compact and space-saving design: The flexible sections can be folded or routed to fit in tight spaces, reducing the overall footprint of the PCB.
- Improved reliability: The flexible sections can withstand flexing, bending, and vibration better than traditional rigid PCBs.
- Enhanced functionality: Rigid-flex PCBs can integrate both rigid and flexible components, enabling more complex and versatile circuit designs.
- Reduced assembly time: The flexible sections can be pre-assembled and then folded or connected to the rigid sections, streamlining the manufacturing process.
Rigid-flex PCBs are commonly used in applications where space is limited, such as in medical devices, wearable electronics, aerospace and defense systems, and portable electronics.
Can you provide some examples of products that utilize rigid-flex PCB technology?
Certainly, here are some examples of products that utilize rigid-flex PCB technology:
1. Smartphones and Tablets:
- Rigid-flex PCBs are used to connect the main board to the display, camera, and other components in a compact package.
- The flexible sections allow for the components to be arranged and folded to fit the slim and curved designs of modern smartphones and tablets.
2. Wearable Devices:
- Rigid-flex PCBs are used in smartwatches, fitness trackers, and other wearable electronics to integrate the circuits and sensors while allowing the device to conform to the user's body.
- The flexible sections enable the wearable to bend and flex with the movements of the user.
3. Medical Devices:
- Rigid-flex PCBs are used in medical equipment, such as endoscopes, catheters, and prosthetic limbs, where the flexibility is crucial for navigating through the human body.
- The rigid sections provide support for the electronic components, while the flexible sections allow the device to be maneuvered and inserted into tight spaces.
4. Aerospace and Defense:
- Rigid-flex PCBs are used in avionics, satellite systems, and military equipment where weight, size, and reliability are critical factors.
- The flexible sections can help route the circuits around complex geometries and accommodate vibrations and movement.
5. Automotive Electronics:
- Rigid-flex PCBs are used in automotive infotainment systems, driver assistance technologies, and other vehicle electronics, where the flexibility allows for better integration and packaging within the limited space.
- The flexible sections can conform to the curved surfaces and tight spaces within the vehicle's interior and under the hood.
6. Industrial Machinery:
- Rigid-flex PCBs are used in industrial automation equipment, such as robotic arms and CNC machines, where the flexible sections enable the circuits to move with the mechanical components.
- This integration of rigid and flexible elements improves the overall reliability and performance of the equipment.
These are just a few examples of the diverse applications where rigid-flex PCB technology is utilized to meet the demands of modern electronic products and systems.
There are several reasons why rigid-flex PCBs are considered a more difficult technology:
You're right, rigid-flex PCBs are considered a more challenging and complex technology compared to traditional rigid PCBs. There are several reasons why rigid-flex PCBs are considered a more difficult technology:
1. Design Complexity:
- Designing a rigid-flex PCB requires careful consideration of the placement and routing of components across the rigid and flexible sections.
- Ensuring proper interconnections between the rigid and flexible layers, as well as managing the mechanical stresses, can be quite complex.
- The design process often involves advanced CAD software and specialized knowledge to optimize the layout and ensure reliability.
2. Manufacturing Challenges:
- Fabricating rigid-flex PCBs requires specialized manufacturing equipment and processes, which are more complex and costly compared to standard rigid PCBs.
- Ensuring proper lamination, plating, and assembly of the rigid and flexible layers can be challenging and requires tight process control.
- Defects, such as delamination or poor interconnections, can be more common in rigid-flex PCBs due to the increased complexity.
3. Testing and Reliability:
- Rigid-flex PCBs need to undergo more extensive testing to ensure reliable performance, including flexibility, bending, and environmental testing.
- Verifying the integrity of the interconnections and the overall mechanical integrity of the assembly is crucial but can be more difficult compared to rigid PCBs.
- Predicting the long-term reliability of rigid-flex PCBs under various operating conditions can be more challenging.
4. Design Constraints:
- The use of flexible materials and the need for interconnections between rigid and flexible sections can introduce design constraints, such as limitations on component placement, routing, and layer counts.
- Balancing the mechanical and electrical requirements can be a delicate process, requiring trade-offs and careful considerations.
5. Supply Chain and Availability:
- The specialized manufacturing capabilities and equipment required for rigid-flex PCBs can limit the number of suppliers and introduce supply chain challenges.
- This can result in longer lead times, higher costs, and potential availability issues compared to standard rigid PCBs.
Despite these challenges, rigid-flex PCBs have become an essential technology for many modern electronic products due to the benefits they offer in terms of size, weight, and functionality. However, it is crucial for design teams to have a deep understanding of the design, manufacturing, and testing considerations to successfully implement rigid-flex PCB technology in their products.
Categories
Latest News
Contact Us
Contact: Ms Tracy
Phone:
Tel:
Add: BludingA,Shixiaganglian Industrial Park,Shajing,Baoan,Shenzhen,China



 Tracy
Tracy