News
Blind and Buried vias definition
Blind and Buried vias
Blind vias: Blind vias are the type of vias that connect the PCB inner trace to the PCB surface trace, which does not penetrate the entire board.
Buried vias: Buried vias are types of vias that connect only the traces between the inner layers, so they are not visible from the PCB surface.
With the current design of portable products in the direction of miniaturization and high-density development, PCB design is also more and more difficult, so PCB production process requirements higher and higher . Most of the portable products with BGA space less then 0.65mm , are using the blind buried hole design process
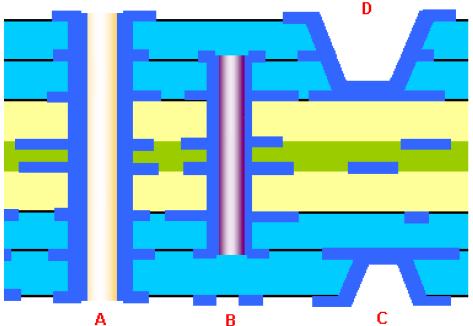
Below is an 8-layer structure of the cross-section diagram:
A: Through-hole (L1-L8)
B: buried hole (L2-l7)
C: blind hole (L7-L8)
D: blind hole (L1-L3)
Bline buried hole PCB
When PCB space is limited, or you're working with tight plated through hole constraints, Blind and Buried Vias may be the answer.
Blind & Buried Via technology has played a pivotal role in squeezing more capability into a smaller space. By shortening vias to only pass through necessary layers, more surface area become available for components.
Key benefits include:
Ability to meet the density constraints of lines and pads on a typical design without increasing the layer count or board size
PCB aspect ratio reduction
Blind and Buried vias introduction:
In printed circuit board design, a via consists of two pads in corresponding positions on different layers of the board, that are electrically connected by a hole through the board. The hole is made conductive by electroplating, or is lined with a tube or a rivet. High-density multi-layer PCBs may have microvias: blind vias are exposed only on one side of the board, while buried vias connect internal layers without being exposed on either surface. Thermal vias carry heat away from power devices and are typically used in arrays of about a dozen.
A via consists of:
Barrel — conductive tube filling the drilled hole
Pad — connects each end of the barrel to the component, plane or trace
Antipad — clearance hole between barrel and metal layer to which it is not connected
A via may be at the edge of the board so that it is cut in half when the board is separated; this is known as a castellated hole and is used for a variety of reasons, including allowing one PCB to be soldered to another in a stack.[1]
Three major kinds of vias are shown in right figure. Basic steps of making PCB is repetition of layer stacking - through drilling of stacked one and plating - copper trace patterning using photolithography and etching. It means without depth-controlled drilling technique such as using laser, possible vias are limited depending on a way of layer stacking. PCB manufacturing typically starts with so called core, basic double-sided PCB. More than two layers are stacked from this basic building block. If two more layers are consecutively stacked from bottom of core, you can have 1-2 via, 1-3 via and through hole. Each type of via is made by drilling at each stacking stage. If one layer is firstly stacked on top of the core and other is stacked from bottom, possible vias are 1-3, 2-3 and through hole. So user must gather information of allowed way of PCB stacking or possible vias from PCB manufacturer. For cheap price, only through holes are made and antipad (or called clearance) are placed on layers which are supposed not to be contacted to vias.
Categories
Latest News
Contact Us
Contact: Ms Tracy
Phone:
Tel:
Add: BludingA,Shixiaganglian Industrial Park,Shajing,Baoan,Shenzhen,China
 Tracy
Tracy