Printed Circuit Boards
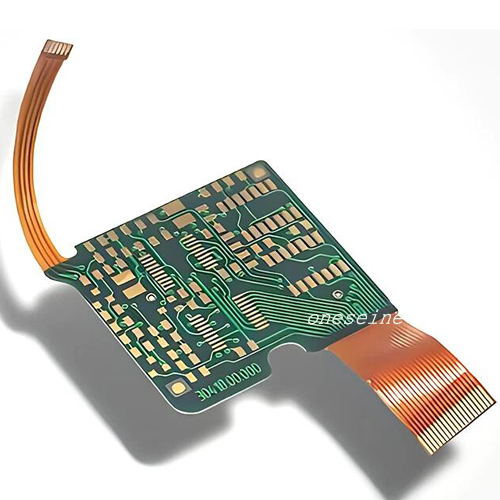
Multilayer Green Rigid Flex 8 Layer Fr4 PCB Printed Circuit Board
- flex pcb manufacturer
- rigid flex pcb
- flex pcb prototype
- semi flex pcb
- Product description: flex pcb design flexpcb fast turn rigid flex pcb flex circuit manufacturer rigid flex board flexible pcb board pcbway flex pcb rigid pcb flexible printed circuit board pcbway flexible pcb fa
Multilayer Green Rigid Flex 8 Layer Fr4 PCB printed circuit board
PCB parameter:
Material: Polymide+FR4(rigid)
Number of layers: 8
Plate thickness: 0.13mm
Minimum aperture: 0.2
Minimum line width/line spacing: 0.1mm
Copper thickness: 1OZ
Surface technology: ENIG
Brand:Oneseine
Solder resistance: Green for rigid,yellow for flex
Flexible PCB concept:
Flexible printed circuit board , also known as "FPC soft board" is made of flexible insulating substrate printed circuit, with a lot of advantage that rigid printed circuit board does not have .
For example, it can be free to bend, winding, folding, can be arranged in accordance with the requirements of any spatial arrangement, and in any three-dimensional space to move and stretch, so as to achieve the integration of component assembly and wire connections. The use of FPC can greatly reduce the volume of electronic products, and suit for high-density, small, highly reliable needs. Therefore, FPC in the aerospace, military, mobile communications, notebook computers, computer peripherals, PDA, digital cameras and other fields or products have been widely used.
Flexible electronics, also known as flex circuits, is a technology for assembling electronic circuits by mounting electronic devices on flexible plastic substrates, such as polyimide, PEEK or transparent conductive polyester film. Additionally, flex circuits can be screen printed silver circuits on polyester. Flexible electronic assemblies may be manufactured using identical components used for rigid printed circuit boards, allowing the board to conform to a desired shape, or to flex during its use. An alternative approach to flexible electronics suggests various etching techniques to thin down the traditional silicon substrate to few tens of micrometers to gain reasonable flexibility (~ 5 mm bending radius)
Advantage of FPCs
Potential to replace multiple rigid boards and/or connectors
Single-Sided circuits are ideal for dynamic or high-flex applications
Stacked FPCs in various configurations
Disadvantages of FPCs
Cost increase over rigid PCBs
Increased risk of damage during handling or use
More difficult assembly process
Repair and rework is difficult or impossible
Generally worse panel utilization resulting in increased cost
FPC Manufacturing
Flexible printed circuits (FPC) are made with a photolithographic technology. An alternative way of making flexible foil circuits or flexible flat cables (FFCs) is laminating very thin (0.07 mm) copper strips in between two layers of PET. These PET layers, typically 0.05 mm thick, are coated with an adhesive which is thermosetting, and will be activated during the lamination process. FPCs and FFCs have several advantages in many applications:
Tightly assembled electronic packages, where electrical connections are required in 3 axes, such as cameras (static application).
Electrical connections where the assembly is required to flex during its normal use, such as folding cell phones (dynamic application).
Electrical connections between sub-assemblies to replace wire harnesses, which are heavier and bulkier, such as in cars, rockets and satellites.
Electrical connections where board thickness or space constraints are driving factors.
Polyimide is a widely used flexible substrate material for flex circuit prototyping and manufacturing, and it offers several key advantages:
oneseine
1. Superior Flexibility and Durability:
- Polyimide has excellent flexibility, allowing it to withstand repeated bending and flexing without cracking or breaking.
- It has a high resistance to fatigue, making polyimide-based flex circuits suitable for applications with dynamic flexing requirements.
2. Thermal Stability:
- Polyimide has a high glass transition temperature (Tg) and can operate at elevated temperatures, typically up to 260°C.
- This thermal stability makes polyimide suitable for applications with high-temperature environments or processes, such as soldering.
3. Excellent Electrical Properties:
- Polyimide has a low dielectric constant and dissipation factor, which helps maintain signal integrity and minimizes crosstalk in high-frequency applications.
- It also exhibits high insulation resistance and dielectric strength, enabling the use of fine-pitch traces and high-density circuits.
4. Chemical and Environmental Resistance:
- Polyimide is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, solvents, and environmental factors, such as moisture and UV exposure.
- This resistance makes polyimide-based flex circuits suitable for applications in harsh environments or where they may be exposed to various chemicals.
5. Dimensional Stability:
- Polyimide has a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), which helps maintain dimensional stability and minimize distortion during fabrication and assembly.
- This property is particularly important for achieving high-precision, high-density circuits.
6. Availability and Customization:
- Polyimide-based flex circuit materials are widely available from various suppliers, making them accessible for prototyping and production.
- These materials can also be customized in terms of thickness, copper foil weight, and other specifications to meet specific design requirements.
The combination of superior mechanical, thermal, electrical, and environmental properties makes polyimide an excellent choice for flex circuit prototyping and production, particularly for applications that require high reliability, flexibility, and performance.
Here are some key keywords related to flexible printed circuit boards (flex PCBs):
1. Flexibility/Bendability
- Bend radius
- Flexural fatigue
- Folding/rolling
2. Substrate Materials
- Polyimide (PI)
- Polyester (PET)
- Polyethylene terephthalate (PET)
- Liquid crystal polymer (LCP)
3. Electrical Properties
- Dielectric constant
- Dissipation factor
- Impedance
- Signal integrity
- Crosstalk
4. Thermal Characteristics
- Glass transition temperature (Tg)
- Coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE)
- Heat resistance
5. Fabrication Processes
- Photolithography
- Etching
- Plating
- Laser cutting
- Multilayer construction
6. Design Considerations
- Trace/space requirements
- Via placement
- Strain relief
- Rigid-flex integration
7. Applications
- Wearable electronics
- Medical devices
- Aerospace and defense
- Automotive electronics
- Consumer electronics
8. Standards and Specifications
- IPC-2223 (Flexible Circuits Design Guide)
- IPC-6013 (Qualification and Performance Specification for Flexible Printed Boards)
9. Testing and Reliability
- Flexural testing
- Environmental testing
- Lifetime predictions
- Failure modes
10. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
- Prototyping
- Volume production
- Material suppliers
- Contract manufacturers
These keywords cover the key aspects of flex PCBs, including materials, design, fabrication, applications, and industry standards. Familiarity with these terms can help you navigate the flex PCB ecosystem more effectively.
Here's an overview of the flex PCB manufacturing process and some of the key challenges involved:
1. Design and Preparation:
- Flex PCB design considerations, such as trace/space requirements, via placement, and rigid-flex integration.
- Creation of detailed design files, including Gerber data, bill of materials, and assembly drawings.
- Selection of appropriate flexible substrate materials (e.g., polyimide, polyester) based on the application requirements.
2. Photolithography and Etching:
- Application of photoresist on the flexible substrate.
- Exposure and development of the photoresist to create the desired circuit pattern.
- Copper etching to remove unwanted copper and form the circuit traces.
- Challenges: Maintaining dimensional accuracy and avoiding undercut during etching.
3. Plating and Finishing:
- Electroplating of the copper traces to increase thickness and improve conductivity.
- Application of surface finishes, such as ENIG (Electroless Nickel Immersion Gold) or HASL (Hot Air Solder Leveling).
- Challenges: Ensuring uniform plating and avoiding defects or discoloration.
4. Multilayer Construction (if applicable):
- Lamination of multiple flexible layers with conductive and dielectric materials.
- Drilling and plating of vias to establish electrical connections between layers.
- Challenges: Controlling registration and alignment between layers, managing layer-to-layer insulation.
5. Cutting and Shaping:
- Precise cutting and shaping of the flex PCB using techniques like laser cutting or die-cutting.
- Challenges: Maintaining dimensional accuracy, avoiding material deformation, and ensuring clean cuts.
6. Assembly and Testing:
- Placement of electronic components on the flex PCB using techniques like surface mount or integrated assembly.
- Electrical testing to ensure the integrity of the circuit and compliance with design specifications.
- Challenges: Handling the flexibility of the substrate during assembly, maintaining solder joint reliability, and performing accurate testing.
7. Packaging and Protective Measures:
- Application of protective coatings, encapsulation, or stiffeners to enhance the durability and reliability of the flex PCB.
- Challenges: Ensuring compatibility between the protective measures and the flex PCB materials, maintaining flexibility, and avoiding delamination.
Key Challenges in Flex PCB Manufacturing:
- Maintaining dimensional accuracy and avoiding distortion during the fabrication process
- Ensuring reliable electrical connections and minimizing signal integrity issues
- Addressing adhesion and delamination concerns between layers and components
- Handling the flexibility and fragility of the substrate during various manufacturing stages
- Optimizing the manufacturing process to achieve high yields and consistent quality
Overcoming these challenges requires specialized equipment, processes, and expertise in flex PCB design and manufacturing. Collaboration with experienced flex circuit manufacturers can help navigate these complexities and ensure the successful production of reliable, high-performance flex PCBs.
Categories
Latest News
Contact Us
Contact: Ms Tracy
Phone:
Tel:
Add: BludingA,Shixiaganglian Industrial Park,Shajing,Baoan,Shenzhen,China


 Tracy
Tracy