Printed Circuit Boards
Advanced Flex Circuit Materials PCB Technology for Aerospace and Military Applications
- flex pcb manufacturer
- flex circuit
- quick turn flex pcb
- flexible printed circuit
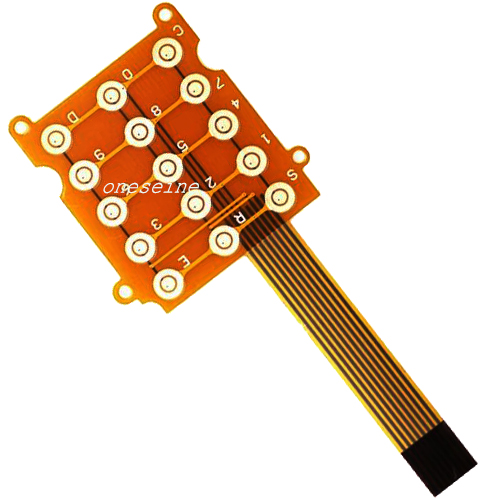
- Product description: flexible pcb printing pcbway rigid flex flex pcb jlcpcb advanced circuits flex pcb rigid flex pcb cost pcbway flex allflex pcb flexible printed circuit manufacturers flex circuit thickness fl
Advanced Flex Circuit Materials PCB Technology for Aerospace and Military Applications
PCB parameter:
Layer:3
Brand:Oneseine
Product Type: Special Flex PCB
Surface finish:ENIG
Applications: Communication electronic equipment
Material: PI,Copper,adhesive
Line width and line spacing:0.1mm/0.1mm
Board thickness:0.45mm +/- 0.03mm
Minimum hole:0.1mm
Flexible circuit board materials
1. Polyimide (PI)
Polyimide is one of the most commonly used substrates for flexible circuit boards. This material has good high temperature resistance and chemical stability, can work in a wide temperature range, and its mechanical properties and dimensional stability are also very good. Therefore, flexible circuit boards made of polyimide are widely used in aerospace, medical devices, handheld devices and wearable devices.
2. Polyamide (PA)
Polyamide is a relatively new flexible circuit board material with simple processing technology and excellent chemical stability. This material is softer than polyimide, so it can be folded and bent with more complex curvatures. The disadvantage of polyamide compared to polyimide is that it has poor high temperature resistance, but this does not affect its application in some scenarios.
3. Polyethylene Terephthalate Glycol (PETG)
Polyethylene terephthalate is a widely used plastic material, and is also widely used in the field of flexible circuit boards. PETG material has excellent mechanical properties and dimensional stability, and its flexibility is also very good. It can resist corrosion from certain chemicals, but its high temperature resistance is somewhat inferior to that of polyamide and polyimide.
4. Other materials
In addition to the above materials, there are other materials for flexible circuit boards, such as polyester, polyether, etc. These materials are relatively less used, but they still have a certain place in some special scenarios.
In summary, different flexible circuit board materials have different characteristics and application scenarios. Choosing the right material can achieve better application results. With the continuous development of flexible electronic technology, the materials of flexible circuit boards will become more and more diversified in the future, and more suitable for various application scenarios.
Flexible Circuit Board PCB Fabrication Process:
1. Cutting: Cutting of hard board base material: Cut a large area of copper-clad board into the size required by the design.
2. Cutting the flexible board base material: Cut the original roll material (base material, pure glue, covering film, PI reinforcement, etc.) into the size required by the engineering design.
3. Drilling: Drill through holes for circuit connections.
4. Black hole: Use potion to make the toner adhere to the hole wall, which plays a good role in connection and conduction.
5. Copper plating: Plate a layer of copper in the hole to achieve conduction.
6. Alignment exposure: Align the film (negative) under the corresponding hole position where the dry film has been pasted to ensure that the film pattern can correctly overlap with the board surface. The film pattern is transferred to the dry film on the board surface through the principle of light imaging.
7. Development: Use potassium carbonate or sodium carbonate to develop the dry film in the unexposed areas of the circuit pattern, leaving the dry film pattern in the exposed area.
8. Etching: After the circuit pattern is developed, the exposed area of the copper surface is etched away by the etching solution, leaving the pattern covered by the dry film.
9. AOI: Automatic optical inspection. Through the principle of optical reflection, the image is transmitted to the equipment for processing, and compared with the set data, the open and short circuit problems of the line are detected.
10. Lamination: Cover the copper foil circuit with an upper protective film to prevent circuit oxidation or short circuit, and at the same time function as insulation and product bending.
11. Laminating CV: Press the pre-laminated covering film and reinforced plate into a whole through high temperature and high pressure.
12. Punch: Use the mold and the power of the mechanical punch to punch the work plate into the shipping size that meets the customer's production requirements.
13. Lamination (superposition of rigid-flex pcb boards)
14. Pressing: Under vacuum conditions, the product is gradually heated, and the soft board and hard board are pressed together through hot pressing.
15. Secondary drilling: Drill the via hole connecting the soft board and the hard board.
16. Plasma cleaning: Use plasma to achieve effects that conventional cleaning methods cannot achieve.
17. Immersed copper (hard board): A layer of copper is plated in the hole to achieve conduction.
18. Copper plating (hard board): Use electroplating to thicken the thickness of hole copper and surface copper.
19. Circuit (dry film): Paste a layer of photosensitive material on the surface of the copper-plated plate to serve as a film for pattern transfer. Etching AOI wiring: Etching away all the copper surface except the circuit pattern, etching out the required pattern.
20. Solder mask (silk screen): Cover all lines and copper surfaces to protect the lines and insulate.
21. Solder mask (exposure): The ink undergoes photopolymerization, and the ink in the screen printing area remains on the board surface and solidifies.
22. Laser uncovering: Use a laser cutting machine to perform a specific degree of laser cutting on the position of the rigid-flex junction lines, peel off theflexible board part, and expose the soft board part.
23. Assembly: Paste steel sheets or reinforcements on the corresponding areas of the board surface to bond and increase the hardness of important parts of the FPC.
24. Test: Use probes to test whether there are open/short circuit defects to ensure product functionality.
25. Characters: Print marking symbols on the board to facilitate the assembly and identification of subsequent products.
26. Gong plate: Use CNC machine tools to mill out the required shape according to customer requirements.
27. FQC: The finished products will be fully inspected for appearance according to customer requirements, and defective products will be picked out to ensure product quality.
28. Packaging: The boards that have passed the full inspection will be packed according to customer requirements and shipped to the warehouse
SHAPE \* MERGEFORMAT
Oneseine Flexible PCB & Rigid-Flex PCB Process Capability
|
Category |
Process Capability |
Category |
Process Capability |
|
Production Type |
Single layer FPC / Double layers FPC Multi-layer FPC / Aluminum PCBs Rigid-Flex PCB |
Layers Number |
1-30 layers FPC 2-32 layers Rigid-FlexPCB 1-60 layers Rigid PCB HDI Boards |
|
Max Manufacture Size |
Single layer FPC 4000mm Double layers FPC 1200mm Multi-layers FPC 750mm Rigid-Flex PCB 750mm |
Insulating Layer Thickness |
27.5um /37.5/ 50um /65/ 75um / 100um / 125um / 150um |
|
Board Thickness |
FPC 0.06mm - 0.4mm Rigid-Flex PCB 0.25 - 6.0mm |
Tolerance of PTH Size |
±0.075mm |
|
Surface Finish |
Immersion Gold/Immersion Silver/Gold Plating/Tin Plating/OSP |
Stiffener |
FR4 / PI / PET / SUS / PSA/Alu |
|
Semicircle Orifice Size |
Min 0.4mm |
Min Line Space/ width |
0.045mm/0.045mm |
|
Thickness Tolerance |
±0.03mm |
Impedance |
50Ω-120Ω |
|
Copper Foil Thickness |
9um/12um / 18um / 35um 70um/100um |
Impedance Controlled Tolerance |
±10% |
|
Tolerance of NPTH Size |
±0.05mm |
The Min Flush Width |
0.80mm |
|
Min Via Hole |
0.1mm |
Implement Standard |
GB / IPC-650 / IPC-6012 / IPC-6013II / IPC-6013III |
Polyimide is a widely used flexible substrate material for flex circuit prototyping and manufacturing, and it offers several key advantages:
oneseine
1. Superior Flexibility and Durability:
- Polyimide has excellent flexibility, allowing it to withstand repeated bending and flexing without cracking or breaking.
- It has a high resistance to fatigue, making polyimide-based flex circuits suitable for applications with dynamic flexing requirements.
2. Thermal Stability:
- Polyimide has a high glass transition temperature (Tg) and can operate at elevated temperatures, typically up to 260°C.
- This thermal stability makes polyimide suitable for applications with high-temperature environments or processes, such as soldering.
3. Excellent Electrical Properties:
- Polyimide has a low dielectric constant and dissipation factor, which helps maintain signal integrity and minimizes crosstalk in high-frequency applications.
- It also exhibits high insulation resistance and dielectric strength, enabling the use of fine-pitch traces and high-density circuits.
4. Chemical and Environmental Resistance:
- Polyimide is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, solvents, and environmental factors, such as moisture and UV exposure.
- This resistance makes polyimide-based flex circuits suitable for applications in harsh environments or where they may be exposed to various chemicals.
5. Dimensional Stability:
- Polyimide has a low coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE), which helps maintain dimensional stability and minimize distortion during fabrication and assembly.
- This property is particularly important for achieving high-precision, high-density circuits.
6. Availability and Customization:
- Polyimide-based flex circuit materials are widely available from various suppliers, making them accessible for prototyping and production.
- These materials can also be customized in terms of thickness, copper foil weight, and other specifications to meet specific design requirements.
The combination of superior mechanical, thermal, electrical, and environmental properties makes polyimide an excellent choice for flex circuit prototyping and production, particularly for applications that require high reliability, flexibility, and performance.
Categories
Latest News
Contact Us
Contact: Ms Tracy
Phone:
Tel:
Add: BludingA,Shixiaganglian Industrial Park,Shajing,Baoan,Shenzhen,China



 Tracy
Tracy